SERENITY
SERENITY
Pediatric waiting rooms play a critical role in shaping a child’s experience within healthcare environments. These spaces often serve children who are ill, injured, or awaiting medical procedures—circumstances that can intensify feelings of fear, anxiety, and discomfort. A thoughtfully designed pediatric waiting area should address these emotional challenges by reducing stress, promoting comfort, and fostering a welcoming, child-centric atmosphere. Unfortunately, this ideal is rarely achieved in many existing healthcare facilities.
Traditional pediatric environments frequently neglect the psychological and emotional needs of young patients. Studies have shown that both children and their caregivers report the highest levels of anxiety in waiting areas compared to other parts of pediatric healthcare facilities (Goel et al., 2024). Moreover, the absence of engaging or interactive elements in these spaces often results in heightened boredom and distress, diminishing overall patient satisfaction. Research has demonstrated that incorporating child-friendly design features—such as interactive media—can significantly reduce anxiety in pediatric patients, underscoring the importance of such interventions (Biddiss et al., 2018). Spaces that support play, learning, and emotional expression are vital in alleviating the inherent stress of medical environments.
In response to these challenges, SERENITY, our proposed emotion-responsive space, offers an innovative approach to pediatric care environments. Utilizing advanced facial recognition technology, SERENITY adapts visual, auditory, and lighting stimuli in real time to create immersive, calming experiences tailored to each child's emotional state. This adaptive design not only enhances emotional well-being but also reduces the caregiving burden, paving the way for more supportive, responsive, and human-centered pediatric care spaces.
Problem
Statement
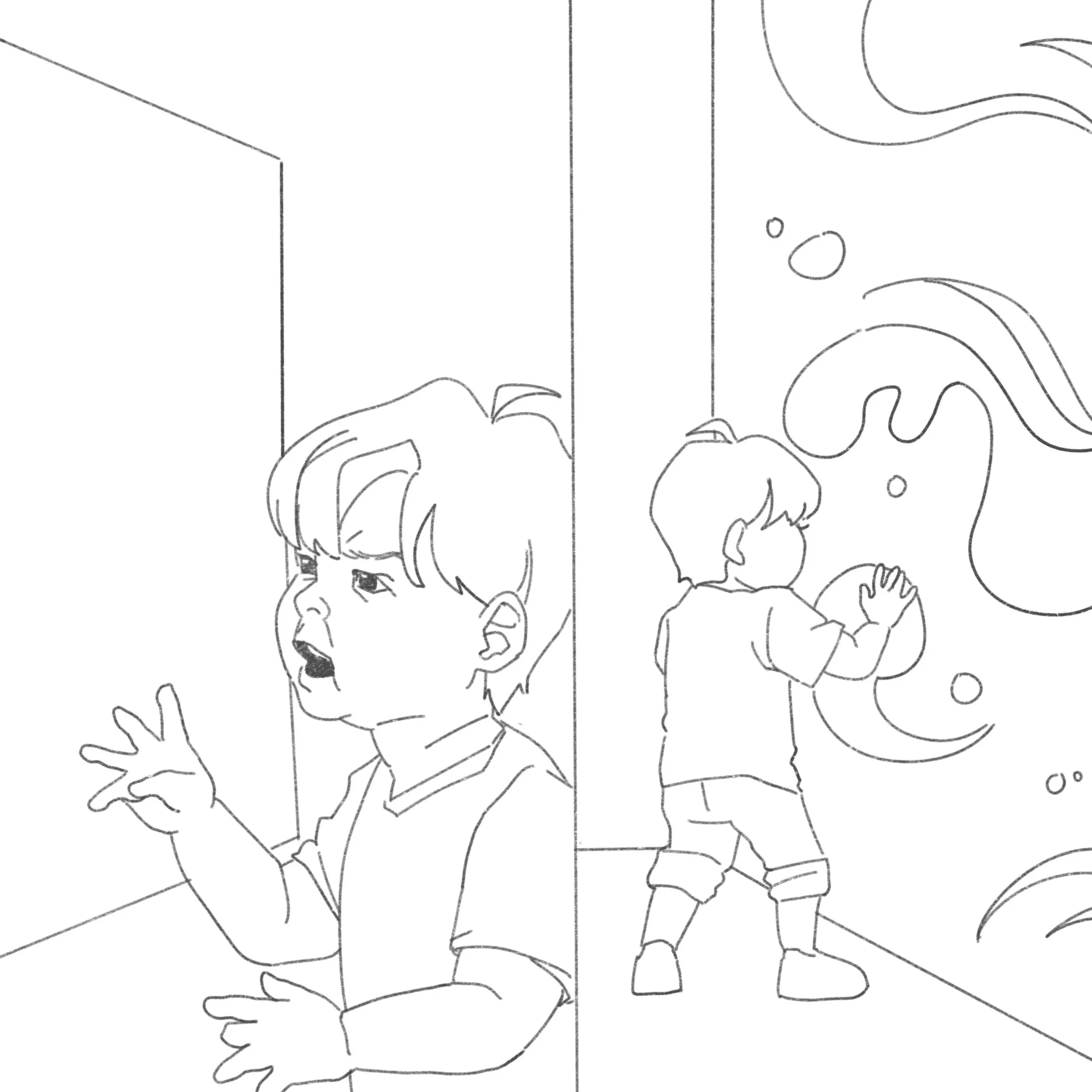
Pediatric waiting and observation rooms play crucial roles in shaping a child's experience in healthcare settings. These spaces should be thoughtfully designed to cater to children's unique needs, reducing anxiety, fostering comfort, and creating a positive, welcoming environment. However, traditional pediatric care spaces often only satisfy their physical needs, overlooking the emotional aspect with reliance on unsanitary toys and manual interventions by caregivers. To address this gap, we propose the development of an interactive, emotion-responsive wall screen system integrated into pediatric hospital rooms and pediatric cells. These screens integrate facial recognition technology to detect children's fluctuating emotions in real-time and adjust the visual, audio, and lighting to create a comforting and engaging atmosphere.
Target Audience: children in pediatric waiting and observation room | ~2-5 ages
Primary Goal: calm and preoccupy children who are anxious and/or in pain
Secondary Goal: use data to create children’s therapy protocols to reduce emotional dissociation from social media/digital interface exposure
Psychology: Attachment Theory, Emotion Dissociation, Self-Concept
Ambient Environment: Adaptive Interface, Lighting Control, Emotional Feedback Loop, Visual Cue, Auditory Cue
Conceptual Framework
Storyboard
“Introducing Serenity, an emotion-driven installation designed to create personalized, responsive environments for toddlers.”
“Parents can track emotional trends, creating a holistic understanding of their child’s well-being.”
“Using facial recognition, Serenity creates dynamic responses that adapt to your child’s emotions in real-time.”
“Serenity adapts to any emotional state, offering comfort, stimulation, and emotional awareness for young children.”
“Serenity detects emotions like happiness, sadness, and anger with facial recognition.”
“Discover how Serenity transforms emotional connection into meaningful experiences for your child.”
“This system uses ambient lighting and projection to foster emotional awareness and well-being.”
Observation Room Layout
Python Scripting

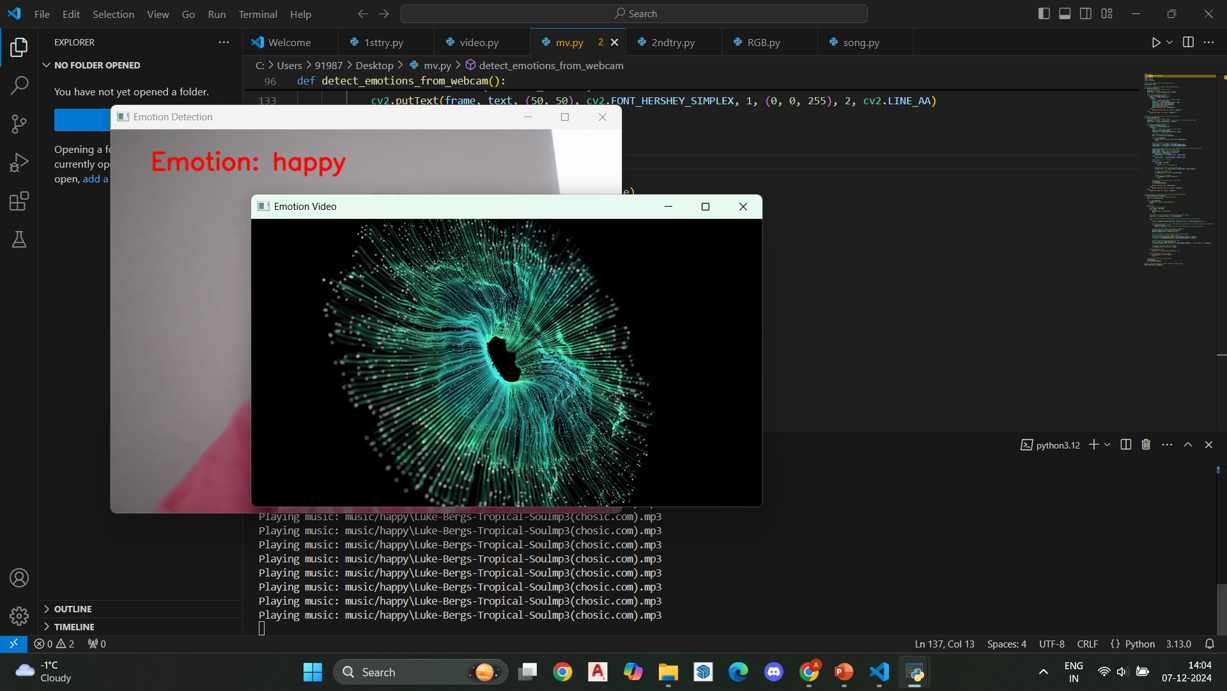




This research introduces an innovative emotion-responsive space designed to support the emotional well-being of pediatric patients in hospitals. Using facial recognition technology, the system detects children's emotions in real-time and adjusts environmental elements—such as visuals, music, and interactive content—to reduce anxiety, promote comfort, and encourage emotional regulation, particularly for children aged 4 to 7. Prototype testing confirms its feasibility and positive impact, demonstrating reduced distress and enhanced psychological resilience during hospital stays. With future development, the system could detect behavioral patterns related to emotional challenges, offering early intervention opportunities for children with autism or developmental delays. Beyond clinical settings, its potential extends to schools and homes as a diagnostic and regulatory tool for caregivers and educators, marking a transformative step in pediatric care and emotional development.










